- Speedtest 1 3 – Quick Easy One Click Connection Testing Near Me
- Speedtest 1 3 – Quick Easy One Click Connection Testing Sites
- Speedtest 1 3 – Quick Easy One Click Connection Testing Tool
- Speedtest 1 3 – Quick Easy One Click Connection Testing Kit
Use Speedtest for quick, easy, one-click connection testingaccurate everywhere thanks to our global network. Free Publisher: Ookla Net Metrics Downloads: 110. Do you want to research connection speed for Easynet?TestMy.net's Download Speed Test and Upload Speed Test log connection information to allow users to research real world Internet speed test results. TestMy.net's speed test database stores information on millions of Internet connections. This tool can average connection speed for any Internet provider, country or city in the world. CLICK TEST / CLICK SPEED TEST Test how fast you can click in 7 different click modes! Clicks in 1/5/10/20/60/100/1000 seconds. Test your CPS now!
How to Test Your Internet Speeds
Testing your internet or WiFi speeds is just a button click away, but before you do there are a few steps to keep in mind to ensure you get the best possible results.
Use a Wired Connection
A wired connection will always provide the fastest speed and best Internet experience. When performing the speed test be sure to connect your computer to your modem using an Ethernet cable:
- Connect the Ethernet cable from the back of the modem to the open Ethernet port on your computer.
- Connect the power cord from the back of the modem to an electrical outlet.
- Check the modem and router lights to confirm they have power, and are connected to the network and your computer.
Remember that every Ethernet cable has a speed limit. Some cables only support speeds up to 10 Mbps, which is slower than most RCN Internet speed packages. Make sure your Ethernet cable can support the speed you've signed up for. If not, you'll need one that will.
Turn off Unused Connected Devices
Be sure to turn off unused devices including laptops, tablets, phones, gaming systems, or other smart home devices. Multiple devices connected to your home network may result in slower internet and WiFi speeds. This is because devices divide bandwidth like a pie, with each device taking the portion it needs at the time of use resulting in slower speeds.
Close all Applications and Programs
Applications or programs running in the background, even when not in use, may be using your internet connection. It is recommended that these programs be closed until after the speed test is completed.
Why do I get a 'socket error' message?
An error may result from having the speed test open in more than one browser tab or window. The test may fail to complete and display the following message:
'A socket error occurred during the Upload test. Please try again later.'
To prevent this error, and get the most accurate test results, close all other browser tabs and windows before running.
If you continue to get a socket error message, or another type of error message, please provide feedback by emailing us at speedtestfeedback@fusionconnect.com. Please, include your OS/Browser information.
Why is the location I usually pick missing from the City list?
We first complete a latency test to our servers, and if a server does not respond within a specified time frame, it is not included in the City list.
A slow response can be caused by latency or packet-loss between the client and server, or particularly high Internet usage (during peak hours). Do try the test again in a little while.
Speedtest 1 3 – Quick Easy One Click Connection Testing Near Me
Movie explorer (in app) 1 8 2. In which browsers does the Speed Test work best?
For best results, use the most recent version of your favorite browser. But at minimum use Firefox 53, Chrome 59, Safari 10, IE 11, or Edge 13 or higher. If you are unable to see Speed Test, though other content appears on the speed test page, check your browser's security setting. Try lowering the setting from High to Medium-High, or even a bit lower, to allow the broadband test application to load.
Why am I receiving 'Could not connect to the Internet' errors when I am connected?
In some cases, firewall and security software can prevent the test from running and generate a 'could not connect' error. Temporarily lowering the severity should allow the broadband test to run. Be sure to turn it back on before leaving our website.
Why didn't the test choose the server location nearest me?
Our Speed Test automatically detects the optimal server host location for testing, which is not necessarily the closest server host. This is due to real-time network circumstances like number of hops, or current traffic load on each test server. Change the selection using the Change City drop down function directly underneath the Start Test button.
Why is my speed lower than expected?
Several factors may slow your connection, resulting in lower-than-expected speeds. Try these simple suggestions below. But if your slower speeds persist, contact your broadband service provider to see if they can determine the issue.
- Be sure to stop any downloads or programs that may be using your connection while running the test.
- When using a wireless connection, there may be wireless interference. Try using a wired Ethernet connection instead.
- Try rebooting your modem or router and then running the test again.
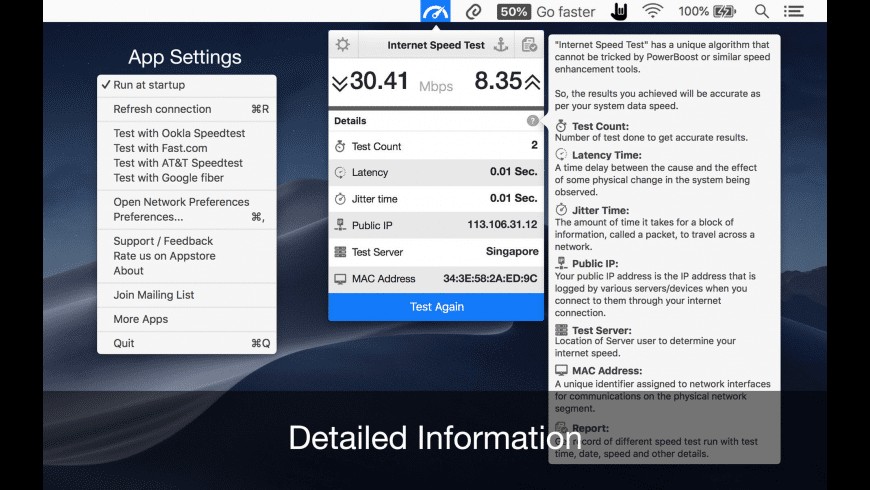
What is 'Throughput' and what factors affect my results?
There are many factors that impact your speed test results. Throughput problems in your local area network, IP or access overhead, and network design all play a role. Please read the definitions and examples below to learn more about these factors.
- Download
Download is a measure of how fast your connection delivers content to your computer or local area network. - Upload
Upload is the measure of how fast content is delivered from your computer or local area network to others on the Internet.
For businesses or power-users, download and upload speed should match or at least be very close. This is important for applications like VoIP, on-line gaming and other interactive programs. Upload speed is even more important if you are operating a server at your location. If achieving optimal upload speed is a concern, consider Ethernet or T1 services. - Kbps
Kbps transfer rate = kilobit per second transfer rate. There are 8 bits in a byte, so we would divide kbps by 8 to get KB/sec transfer rate. - Mbps
Mbps transfer rate = megabits per second transfer rate. 1000 kilobits equals one megabit. One megabit per second equals 1 million bits per second. Mbps is the industry-standard used by ISPs. - MBps
MegaBytes per second. There are 8 megabits in one megabyte. - Transfer Rate
- Transfer rate is speed at which data can be transmitted between devices. As files to download become increasingly larger, the highest data transfer rate is most desirable.
- Throughput
Throughput is the maximum amount of communication or messaging that can be transmitted through a communication channel during an elementary unit of time, usually, in a second.
Depending on the type of channel, the addressing mechanism used in that channel, the type of messages are being transmitted and how secure the transmission needs to be—along with physical attributes like temperature, humidity and signal-to-noise ratios—actual measured throughput will vary.
An Example of Throughput
You have Ethernet 8.0 Mbps service and need to transmit an email which is exactly 1MB in size You may expect it will take exactly 1 second to transmit that message. But it will actually take longer as the total information that needs to be transmitted is more than 1MB. The total information is called Payload. The channel needs to not only transmit the payload but also some addressing details like where it is coming from and where it is destined to.
The device that sends this email will break down the message into smaller pieces and package them into what are called IP Packets. The size of these packets is usually determined by your Local Area Network. Some have smaller size, so the message will take more IP Packets to transmit; while others may have larger size which needs fewer IP Packets. Each IP Packet also contains an IP Header. This is where the information like the source IP Address, the destination IP Address and additional information about the payload is included. IP Header is usually 20 Bytes (160 Bits) long.
Speedtest 1 3 – Quick Easy One Click Connection Testing Sites
Why am I receiving 'Could not connect to the Internet' errors when I am connected?
In some cases, firewall and security software can prevent the test from running and generate a 'could not connect' error. Temporarily lowering the severity should allow the broadband test to run. Be sure to turn it back on before leaving our website.
Why didn't the test choose the server location nearest me?
Our Speed Test automatically detects the optimal server host location for testing, which is not necessarily the closest server host. This is due to real-time network circumstances like number of hops, or current traffic load on each test server. Change the selection using the Change City drop down function directly underneath the Start Test button.
Why is my speed lower than expected?
Several factors may slow your connection, resulting in lower-than-expected speeds. Try these simple suggestions below. But if your slower speeds persist, contact your broadband service provider to see if they can determine the issue.
- Be sure to stop any downloads or programs that may be using your connection while running the test.
- When using a wireless connection, there may be wireless interference. Try using a wired Ethernet connection instead.
- Try rebooting your modem or router and then running the test again.
What is 'Throughput' and what factors affect my results?
There are many factors that impact your speed test results. Throughput problems in your local area network, IP or access overhead, and network design all play a role. Please read the definitions and examples below to learn more about these factors.
- Download
Download is a measure of how fast your connection delivers content to your computer or local area network. - Upload
Upload is the measure of how fast content is delivered from your computer or local area network to others on the Internet.
For businesses or power-users, download and upload speed should match or at least be very close. This is important for applications like VoIP, on-line gaming and other interactive programs. Upload speed is even more important if you are operating a server at your location. If achieving optimal upload speed is a concern, consider Ethernet or T1 services. - Kbps
Kbps transfer rate = kilobit per second transfer rate. There are 8 bits in a byte, so we would divide kbps by 8 to get KB/sec transfer rate. - Mbps
Mbps transfer rate = megabits per second transfer rate. 1000 kilobits equals one megabit. One megabit per second equals 1 million bits per second. Mbps is the industry-standard used by ISPs. - MBps
MegaBytes per second. There are 8 megabits in one megabyte. - Transfer Rate
- Transfer rate is speed at which data can be transmitted between devices. As files to download become increasingly larger, the highest data transfer rate is most desirable.
- Throughput
Throughput is the maximum amount of communication or messaging that can be transmitted through a communication channel during an elementary unit of time, usually, in a second.
Depending on the type of channel, the addressing mechanism used in that channel, the type of messages are being transmitted and how secure the transmission needs to be—along with physical attributes like temperature, humidity and signal-to-noise ratios—actual measured throughput will vary.
An Example of Throughput
You have Ethernet 8.0 Mbps service and need to transmit an email which is exactly 1MB in size You may expect it will take exactly 1 second to transmit that message. But it will actually take longer as the total information that needs to be transmitted is more than 1MB. The total information is called Payload. The channel needs to not only transmit the payload but also some addressing details like where it is coming from and where it is destined to.
The device that sends this email will break down the message into smaller pieces and package them into what are called IP Packets. The size of these packets is usually determined by your Local Area Network. Some have smaller size, so the message will take more IP Packets to transmit; while others may have larger size which needs fewer IP Packets. Each IP Packet also contains an IP Header. This is where the information like the source IP Address, the destination IP Address and additional information about the payload is included. IP Header is usually 20 Bytes (160 Bits) long.
Speedtest 1 3 – Quick Easy One Click Connection Testing Sites
Assuming that this customer uses 100 Byte payload, each IP Packet will now be 120 Bytes long. And that 1MB message will have to be broken down into 10,000 payload pieces. That means to transmit the whole message the channel really needs to transmit about 1,200,000 Bytes or 1.2 MB or 9,600,000 bits. It will take at least 1.2 seconds to transmit all these bytes on this 8 Mbps service assuming that all these IP packets with the payload arrive without any errors and not needing re-transmission. This is called IP Overhead.
Actual Throughput will always be less than line rate of the access service that is communicated by your provider—and this is all based on IP Overhead only. Ethernet services also have a Layer 2 or Ethernet Overhead. Other services may have ATM, Frame Relay or other kinds of Overhead depending on the design. All of this may contribute to a slower bandwidth throughput than what you are expecting.
Other frequent factors influencing throughput:
- The number of devices sharing the access circuit and the activity the other devices are generating while the test is running
- A rogue LAN port that is clogging the LAN with transmission
- A leaky LAN port which degrades LAN performance
- LAN signaling issues which create a lot of packet re-transmission for the devices on the LAN
- LAN Router with performance issues, low processing power or Deep Packet Inspection and advanced security features like URL blocking enabled
- Wireless Access Points on the LAN side
- Distance (both geographical as well as number of hops) between the speed testing client and the server
Why do I see a license expiration notice?
This notice is in place to protect our test from being stolen and run, mirrored, or framed into another website.
To remove this notice:
Make sure you are going to https://www.speakeasy.net/speedtest/. We have software in place to block the test from being used in any other domain.
Speedtest 1 3 – Quick Easy One Click Connection Testing Tool
Also, you may have an older version of the test cached in your browser. Clearing your cache and Fusion Connect cookies should make the license expiration notice disappear.
How does security software and firewalls impact the test?
Our internet broadband test sends packets of empty data back and forth to your computer in order to test your line speed. Since we are a third-party sending a receiving a tiny data packet from your computer to perform the test, some ad block or security services interpret this as an attack and act accordingly. Temporarily lowering the severity should allow the speed test to work. Be sure to turn it back on before leaving our website.
Speedtest 1 3 – Quick Easy One Click Connection Testing Kit
How do I save my bandwidth test results?
Your most recent speed test results are saved in your Results History when tested on desktop or tablet.
